Definition
Where \( \mathbb{P}(A|B) \) is the probability of event \(A\) given that event \(B\) occurs:
$$ \mathbb{P}(A|B) = \frac{\mathbb{P}(A \cap B)}{\mathbb{P}(B)} $$
Notice that if \(P(B) = 0\) then it’s meaningless to condition \(A\) on \(B\).
Satisfying the Axioms of Probability
Axiom 1: Normalization
$$ \mathbb{P}(B|B) = \frac{\mathbb{P}(B \cap B)}{\mathbb{P}(B)} = 1 $$
Axiom 2: Non-negativity
Because \(A \cap B \subseteq B \), then \( 0 \le \mathbb{P}(A|B) \le 1 \).
Axiom 3: Additivity
Let \(A\) and \(C\) be mutually exclusive, then \( \mathbb{P}((A \cup C) | B) = \mathbb{P}(A | B) + \mathbb{P}(C | B) \)
$$ \mathbb{P}((A \cup C) | B) = \frac{ \mathbb{P}((A \cup C) \cap B) }{ \mathbb{P}(B) } $$
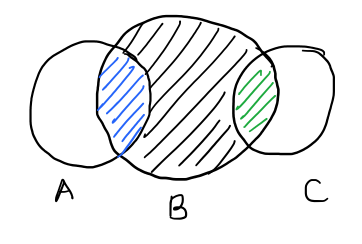
$$ = \frac{ \mathbb{P}(A \cap B) }{\mathbb{P}(B)} + \frac{ \mathbb{P}(C \cap B) }{\mathbb{P}(B)} $$ $$ = \mathbb{P}(A | B) + \mathbb{P}(C | B) $$